Read this if you are working on ESG initiatives at your organization.
Whether you are a director or an executive well into the journey of developing and communicating your company’s strategic sustainability plans or in early stages, the rising public demand for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting is becoming a force that cannot be ignored by boards and management teams.
ESG overview: reminders and FAQs
What does ESG information comprise? The term “ESG” reporting, used broadly, covers qualitative discussions of topics and quantitative metrics used to measure a company’s performance against ESG risks, opportunities, and related strategies. ESG, sustainability, and corporate social responsibility are terms often used interchangeably to describe nonfinancial reporting being shared publicly by companies. Such information is not currently subject to a singular authoritative set of standards.
What are examples of ESG and sustainability information? The following do not represent all-inclusive lists and, while some ESG information may be measured quantitatively, there are often many means to calculate metrics or information that may be difficult to quantify and therefore may be expressed qualitatively and described as such:
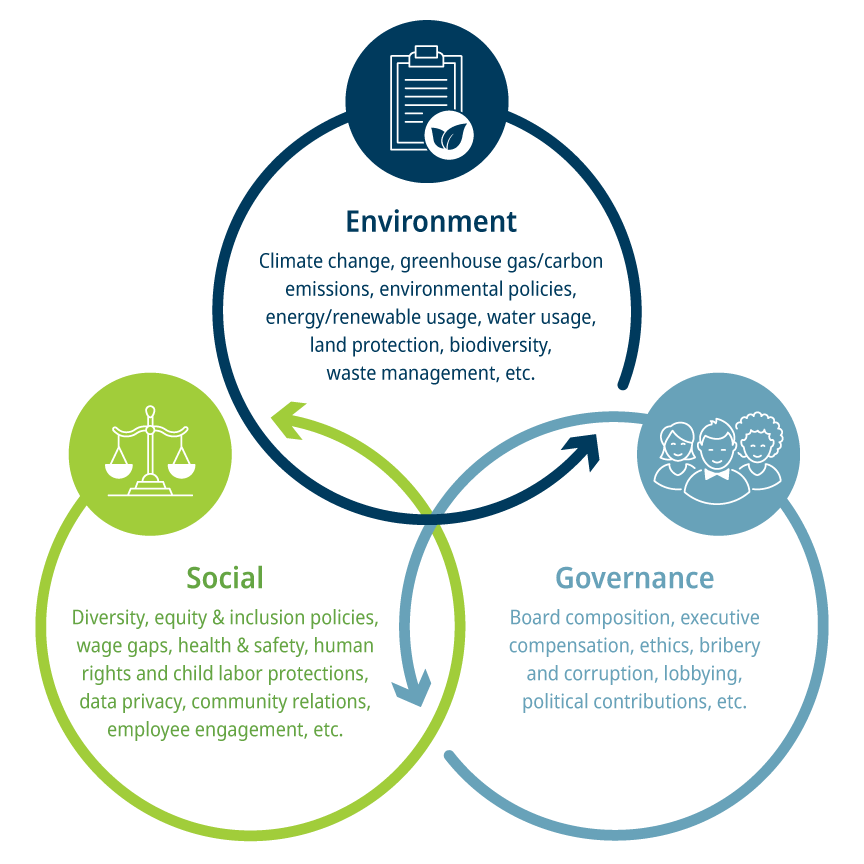
As corporate ESG activities increase in relevance and importance to stakeholders, companies are seeking to both understand the complex landscape of ESG disclosure and reporting and determine the best path forward. This includes identifying, collecting, sharing, and improving upon qualitative and quantitative metrics reflecting long-term, strategic ESG value creation.
Organizations are in various stages of readiness to report on such decision-useful information. Currently, a myriad of reporting frameworks and wide variations in how companies choose to publicly share ESG information exist, making the ESG landscape complex to navigate. However, two things are certain:
- The pressure for companies to publicly disclose their approach to sustainability and ESG reporting continues to mount from a broad variety of stakeholders, and
- ESG is rapidly rising to the forefront of boardroom agendas.
We have prepared the following to provide useful reminders, FAQs, and insights for those charged with governance as they consider the rapidly changing current ESG reporting landscape and evolving regulatory developments.
Is there a single authoritative set of ESG reporting standards?
There are currently several frameworks and standards in use globally by companies to report on ESG, many of which may be complementary and used in combination for external reporting. Some of the more commonly used frameworks are: Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB); Global Reporting Initiative (GRI); Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD); International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC); and Climate Disclosures Standards Board (CDSB). While many of these may already be complementary to each other, there is also growing support for a singular, global set of reporting standards for ESG, though the timing to achieve the necessary convergence remains uncertain.
Are U.S. companies required to disclose ESG information?
Outside of certain industry regulators, such as required reporting by the Environmental Protection Agency on greenhouse gas emissions, implementation by U.S. companies remains voluntary. However, pressure from institutional investors—BlackRock, State Street and Vanguard—is mounting in support of companies providing ESG disclosures that align with both the SASB and TCFD frameworks. Additionally, sustainability risk issues are increasingly integrated into organizational risk frameworks such as COSO’s Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework.
Companies must also assess whether other ESG information, such as climate risk disclosures, are required under current MD&A disclosure rules. For example, if the risk represents a known trend or uncertainty the company reasonably expects will have a material impact on the company’s results of operations or capital resources, additional disclosure would be required.
What companies are reporting, and what information are they reporting?
ESG disclosures vary significantly depending on the nature of the business, geography, industry, and stakeholder base, as well as available resources to devote to ESG. The largest global public companies have led the way in external ESG reporting and engagement, but this reporting is rapidly expanding to encompass smaller public entities and private entities. Companies of all sizes are both feeling the pressure to produce ESG reporting and identifying it as a means to differentiate themselves in the market by proactively conveying their corporate stories and strategies.
As noted in a recent White & Case study of proxy statements and filed 10-Ks for the top 50 companies by revenue in the Fortune 100, the following ESG categories showed the most significant increase in disclosures from the prior year:
- Human capital management (HCM)
- Environmental
- Corporate culture
- Ethical business practices
- Board oversight of environment & social (E&S) issues
- Social impact/community
- E&S issues in shareholder engagement
The study noted that a majority of E&S disclosures in the SEC filings were qualitative and did not provide quantitative metrics. However, disclosures pertaining to environmental, HCM, and E&S goals, along with social impact and community relations were more likely to contain quantitative metrics.
Where do companies report ESG information? The most common places companies are providing public ESG disclosures include:
- Standalone reports including corporate social responsibility (CSR)/sustainability reports
- Company websites and marketing materials
- MD&A sections of annual and quarterly reports
- Earnings calls
- Proxy statements and 8-Ks
Evolving auditor ESG attestation
Many of the metrics and qualitative disclosures around ESG information are not “governed” by an established framework such as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), and thus, may not be subject to the same rigor of processes and controls over such processes to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the underlying data and the appropriateness of the decisions and judgments being made by management in reporting on such information. For example, the fear of corporate “green or impact washing”—the incentive to make stakeholders believe that a company is doing more to promote ESG activities, particularly environmental protections, than it actually is—has left many stakeholders questioning the reliability, consistency, and accuracy of company ESG reporting. As ESG reporting continues to evolve and become a significant consideration for boards, investors, employees, suppliers, lenders, regulators, and others in making business decisions, there is a growing focus on the value of assurance on such information provided by independent third parties.
Type of attestation services to be provided
Determining the scope and level of assurance to be provided will vary based on company objectives in presenting ESG information, management’s readiness, and intended users and uses of ESG information. Attest services may include:
- Examination: Consists of an examination performed by an auditor resulting in an independent opinion indicating whether the ESG information is in accordance with the agreed upon criteria, in all material respects. An examination engagement is the closest equivalent to the reasonable assurance obtained in an audit of financial statements.
- Review: Consists of limited procedures, performed by an auditor, that result in limited assurance. The objective of a review engagement is for the auditor to express a conclusion about whether any material modifications should be made to the ESG information in order for it to be in accordance with the agreed upon criteria. Review engagements are substantially less in scope than examination engagements.
The ESG journey: first steps for boards just beginning the ESG reporting journey
The AICPA and Center for Audit Quality (CAQ) have issued a roadmap for audit practitioners laying out initial steps for those organizations and their boards who are in the beginning phases of the ESG reporting journey:
- Conduct a materiality or risk assessment to determine which ESG topics are prioritized as important or “material” to the organization, its investors and other stakeholders
- Implement appropriate board oversight of material ESG matters
- Integrate/align material ESG topics into the ERM process
- Integrate ESG matters into the overall company strategy
- Implement effective internal control over ESG data collection, processing, and reporting
For boards considering an attestation engagement
The CAQ has further prepared the following questions boards may consider for companies that have already started reporting on ESG and may be considering an attestation engagement:
- What is the purpose and objective of the attestation engagement on ESG information?
- Who are the intended users of the ESG information and related attestation report?
- Why do the intended users want or need an attestation report on the ESG information?
- What are the potential risks associated with a misstatement or omission in the ESG information?
- Does the company have a clear understanding what ESG information the intended users want or need to be in the scope of the attestation engagement?
- What level of attestation service (examination or review engagement) will help the company achieve its objective?
Additional questions for board members to consider regarding their company’s preparedness for reporting include:
- Does management have well established controls, policies, and procedures for the collection of and disclosure of ESG information? Are there gaps to be addressed?
- Has the board, along with management, set specific objectives and goals for external reporting of ESG information?
- Is the information disclosed by the company consistent across its various communication channels?
- Are the ESG responsibilities at the board level clearly defined among appropriate committees and are those responsibilities directly linked to corporate strategic ESG goals and external reporting needs?
- Have the right advisors been identified to assist in preparing for reporting and/or to attest to the quality of reporting?
Next steps
We encourage management, audit committees, and other board members to continue to educate themselves on the evolving landscape of ESG and carefully consider the needs of various stakeholders broadly when mapping out their ESG reporting needs. Particular attention should be paid to regulatory developments in this area.